Non Viral Hepatitis
Non-viral hepatitis is liver inflammation and damage not caused by a viral infection, instead resulting from factors like alcoholic hepatitis from excessive alcohol use, drug-induced hepatitis from medications or toxins, autoimmune hepatitis where the immune system attacks the liver, metabolic disorders, and ischemic hepatitis from poor blood flow to the liver. It is not contagious and may lead to liver scarring, liver failure, or cancer.
Causes of Non-Viral Hepatitis
Alcohol-Related Liver Disease (ALD): Chronic, excessive alcohol consumption damages liver cells, causing inflammation.
Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI): Certain medications (both prescription and over-the-counter), toxins, and even some herbal remedies can cause liver inflammation and damage
Autoimmune Hepatitis : The body’s own immune system mistakenly attacks and damages liver cells, leading to inflammation.
Metabolic Disorders: Conditions that lead to the build-up of harmful substances or abnormal fat storage in the liver can cause inflammation and damage.
Ischemic Hepatitis (Shock Liver) : This occurs when the liver doesn’t receive enough blood flow and oxygen, often due to low blood pressure.
Genetic Disorders
: Some inherited conditions, like Wilson disease or hemochromatosis, can cause toxic products to build up in the blood and damage the liver.
Biliary and Pancreatic Disorders: Problems with the bile ducts or pancreas that obstruct bile flow can also injure the liver.
Alcoholic hepatitis: Caused by excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption, which damages liver cells and causes inflammation. The condition is reversible if alcohol use is stopped.
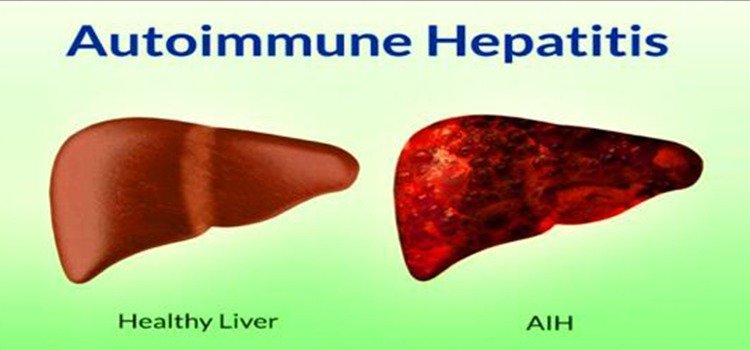
Autoimmune hepatitis: A chronic disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells. It is most common in women and can be managed with immunosuppressive medications.
Toxic or drug-induced hepatitis: Caused by exposure to certain chemicals, toxins, or medications. Treatment involves identifying and discontinuing the offending substance.
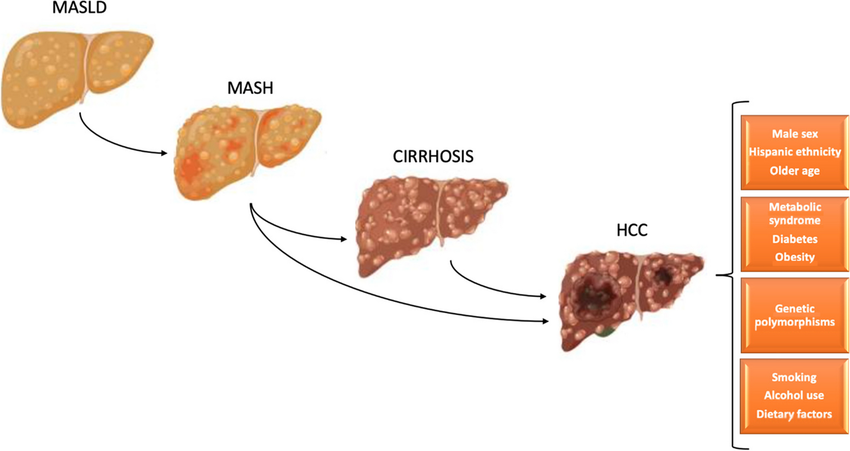
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Caused by excess fat in the liver, which can lead to inflammation and, over time, chronic hepatitis.
Ischemic hepatitis: Also known as “shock liver,” this is caused by inadequate blood supply to the liver, often due to severe low blood pressure or heart failure.
Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
Contagion
Unlike viral hepatitis, which can be spread from person to person, non-viral hepatitis is not contagious because it is not caused by an infectious agent
