Hepatitis
Hepatitis is liver inflammation, most often from viruses (A, B, C, D, E), but also from alcohol, drugs, toxins, or autoimmune conditions, leading to symptoms like fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, and dark urine. Symptoms can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term), with chronic hepatitis potentially causing severe damage like cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer. Transmission, prevention, and treatment vary by type, with some types preventable by vaccines (A, B) or curable with antiviral medications (C)
Hepatitis A is an inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV). The virus is primarily spread when an uninfected (and unvaccinated) person ingests food or water that is contaminated with the faeces of an infected person. The disease is closely associated with unsafe water or food, inadequate sanitation, poor personal hygiene and oral-anal sex.
Unlike hepatitis B and C, hepatitis A does not cause chronic liver disease but it can cause mild to severe symptoms and rarely fulminant hepatitis (acute liver failure), which is often fatal. WHO estimates that in 2016, 7134 persons died from hepatitis A worldwide (accounting for 0.5% of the mortality due to viral hepatitis).
Types of Hepatitis
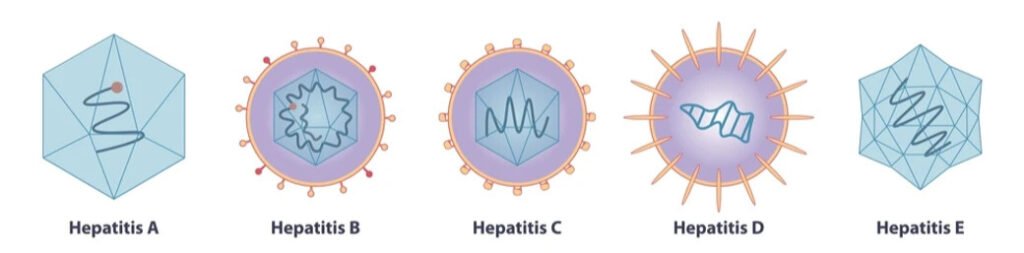
Hepatitis A: Caused by the Hepatitis A Virus (HAV), transmitted through contaminated food and water, and almost always results in a mild, short-term illness that grants lifelong immunity.
Hepatitis B: Caused by the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV), transmitted through infected blood or bodily fluids. Acute infections are common, but it can lead to chronic infection, particularly in children.
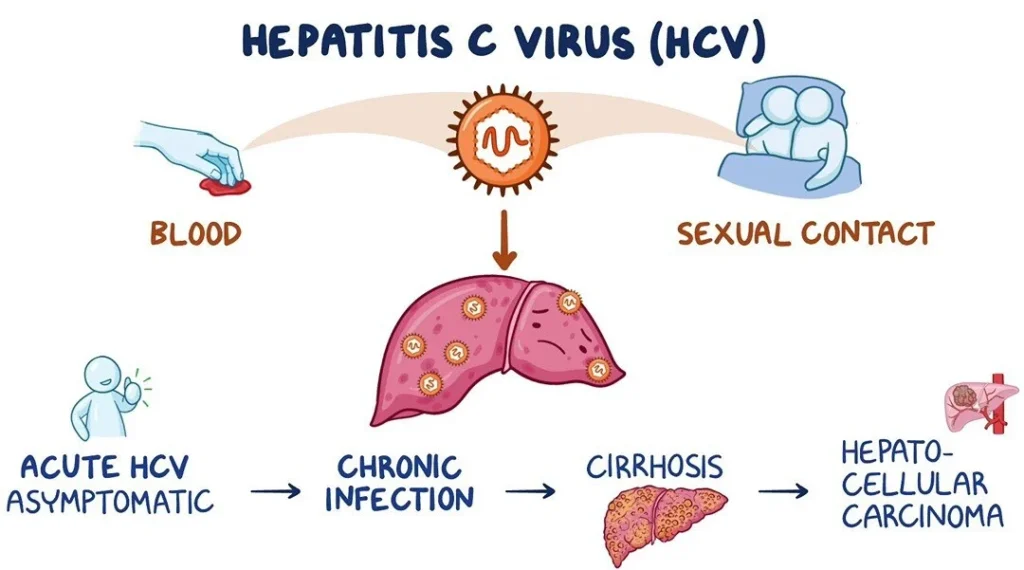
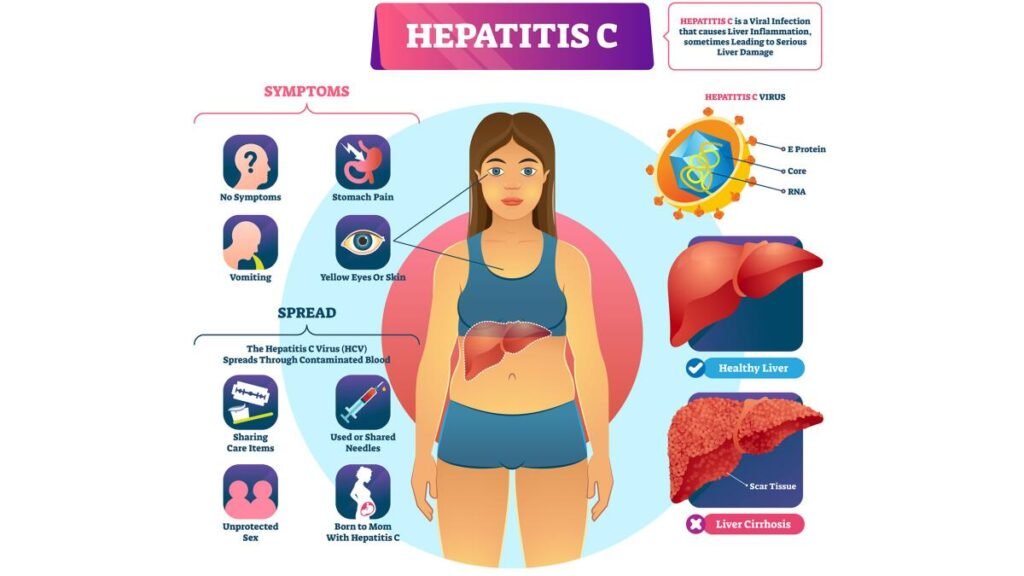
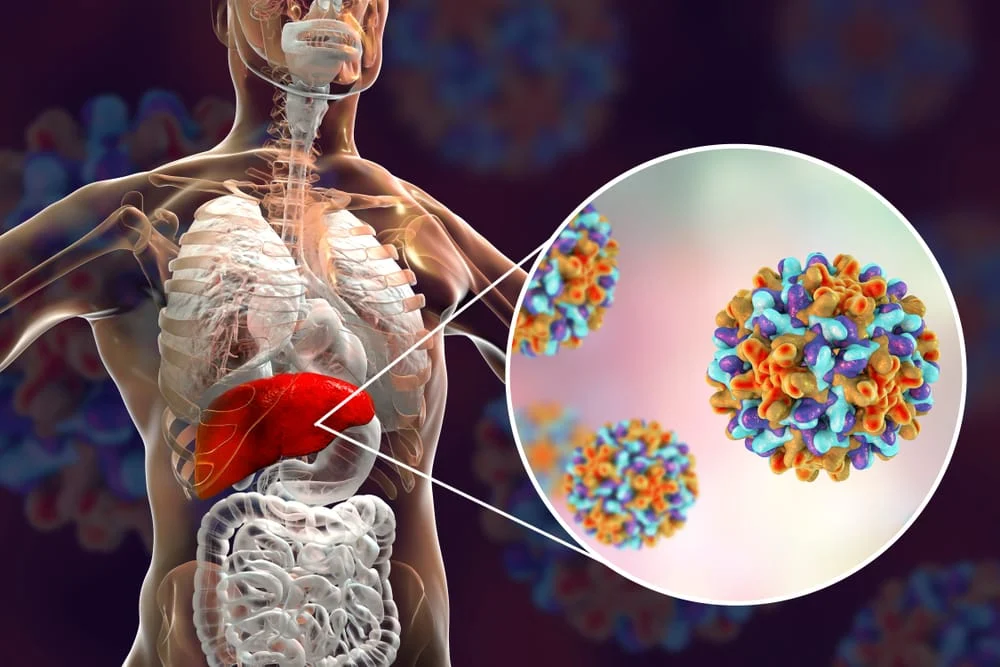
Hepatitis C: Caused by the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV), a bloodborne virus transmitted through shared needles or blood transfusions. It frequently leads to chronic infection.
Hepatitis D: A coinfection with Hepatitis B is required for Hepatitis D to cause illness.
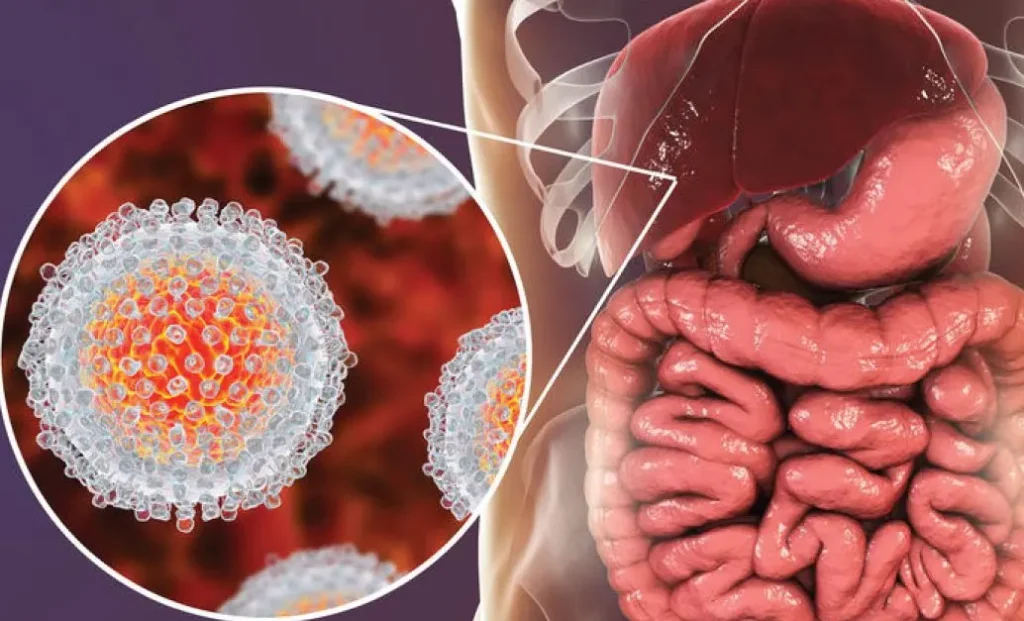
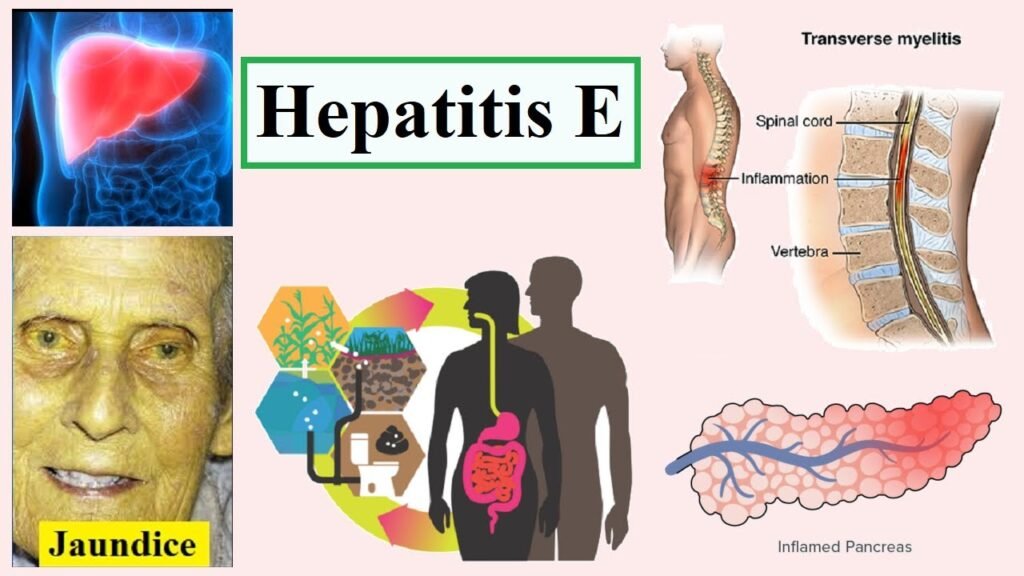
Hepatitis E: Caused by the Hepatitis E Virus (HEV), transmitted through contaminated water and food.
Non-Viral Causes: Hepatitis can also be caused by alcohol, certain medications or chemicals, and other liver diseases or genetic disorders.
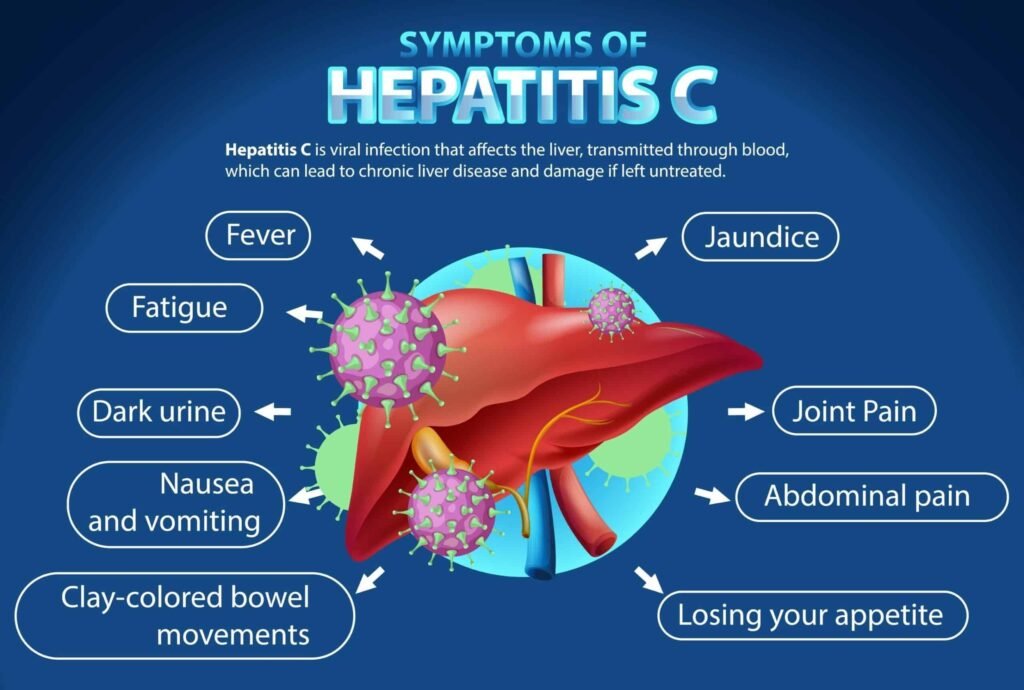
Symptoms
- Fatigue and fever
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side
- Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite
- Dark urine and clay-colored stools
- Joint pain.
Symptoms of hepatitis A range from mild to severe and can include fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark-coloured urine and jaundice (a yellowing of the eyes and skin). Not everyone who is infected will have all the symptoms.
Complications of hepatitis
Chronic hepatitis B or C can lead to more severe health problems. Because the virus affects the liver, people with chronic hepatitis B or C are at risk of:
- chronic liver disease
- cirrhosis
- liver cancer
When your liver stops functioning normally, liver failure can occur. Complications of liver failure include:
- bleeding disorders
- a buildup of fluid in your abdomen, known as ascites
- increased blood pressure in portal veins that enter your liver, known as portal hypertension kidney failure hepatic encephalopathy which can involve fatigue, memory loss, and diminished mental abilities
- hepatocellular carcinoma, which is a form of liver cancer
- death
People with chronic hepatitis B and C should avoid alcohol as it can accelerate liver disease and failure. Certain supplements and medications can also affect liver function. If you have chronic hepatitis B or C, check with your doctor before taking any new medications.
Who is at risk?
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread (high endemicity), most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- Poor sanitation;
- Lack of safe water;
- Living in a household with an infected person;
- Being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection;
- Use of recreational drugs;
- Sex between men; and
- Travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
Reducing exposure
Hepatitis viruses can transmit from person to person through contact with bodily fluids, water, and foods containing infectious agents. Minimizing your risk of contact with these substances can help to prevent contracting hepatitis viruses.
Practicing effective hygiene is one way to avoid contracting hepatitis A and E. The viruses that cause these conditions can be present Trusted in water. If you’re traveling to a country where there is a high prevalence of hepatitis, you should avoid:
- local water
- ice
- raw or undercooked shellfish and oysters
- raw fruit and vegetables
The hepatitis B, C, and D viruses can transmit through contact with bodily fluids containing these infectious agents.
You can reduce your risk Trusted Source of coming into contact with fluids containing these viruses by:
- not sharing needles
- not sharing razors
- not using someone else’s toothbrush
- not touching spilled blood
Hepatitis B and C can carry through sexual intercourse and sexual contact. Using barrier methods, such as condoms and dental dams, during sexual activity can help decrease the risk of infection.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis involves blood tests to identify the specific virus or cause. Treatment varies by type:
Hepatitis A: No specific treatment; supportive care is typically sufficient.
Hepatitis B: Antiviral medications and interferon are used for chronic cases.
Hepatitis C: Modern antiviral drugs can cure most cases of Hepatitis C.
Physical exam, which may or may not reveal a swollen, enlarged liver
Blood tests to check liver enzymes that are elevated when the liver is damaged or infected, as well as blood tests to check for the presence of any of the five viruses causing hepatitis
Ultrasound of the liver to detect any changes
Liver biopsy to confirm suspected inflammation when other tests are inconclusive and to determine the exact degree of liver damage
Tips to prevent hepatitis
There are vaccines that can help protect against many hepatitis viruses. Minimizing your risk of exposure to substances containing these viruses can also be an important preventive measure
Vaccination: Vaccines are available for Hepatitis A and B.
Hygiene: Practicing safe water and sanitation habits is crucial for preventing Hepatitis A.
Safer Practices: Avoid sharing needles and ensure safe medical procedures to prevent Hepatitis B and C.

Vaccines
A vaccine for hepatitis A is available and can help prevent the contraction of HAV. The hepatitis A vaccine is a series of two doses and most children begin vaccination at age 12 to 23 monthsTrusted Source. This is also available for adults and can also include the hepatitis B vaccine.
The CDCTrusted Source recommends hepatitis B vaccinations for all newborns. Doctors typically administer the series of three vaccines over the first 6 months of childhood.
The CDC also recommends the vaccine for all healthcare and medical personnel. Vaccination against hepatitis B can also prevent hepatitis D.
There are currently no vaccines for hepatitis C or E.
