Ischemic Hepatitis
What is Ischemic Hepatitis?
A misnomer: While called “hepatitis” (meaning liver inflammation), the condition involves liver cell death (necrosis) due to lack of oxygen, not inflammation.
Mechanism:It occurs when the liver’s need for blood and oxygen isn’t met.
Common causes:
- Cardiac failure: Weakened heart function reduces blood flow to the liver.
- Shock: Sudden, large drops in blood pressure from severe bleeding, dehydration, or infection can decrease blood flow to the liver.
- Respiratory failure: Low blood oxygen levels can also contribute to liver injury.
- Sepsis: A severe, body-wide infection (sepsis) increases the liver’s need for oxygen and blood, leading to ischemic hepatitis.
Key Characteristics
- Aminotransferase surge: A hallmark is a sudden, massive, and temporary increase in liver enzymes (aminotransferases, like AST and ALT) in the blood.
- Location: Necrosis (cell death) typically occurs in the centrilobular zone of the liver.
- Prognosis: People generally recover if the underlying condition causing hepatic ischemia is treated.
Causes of Ischemic Hepatitis
Ischemic hepatitis develops when the liver does not receive enough blood, oxygen, or both to function properly.
The most common reason is reduced blood flow throughout the body, which may happen due to:
Heart failure
A sudden, severe drop in blood pressure, as in massive bleeding, severe dehydration, or widespread infection (septic shock)
Severely low oxygen levels, often from long-standing or severe respiratory diseases
Sepsis (bodywide infection), which increases the liver’s demand for oxygen and blood
Blood Vessel Blockage
The liver normally has a safety net because it receives blood from two main vessels:
the hepatic artery
the portal vein
Ischemia usually develops only if both are blocked or narrowed. If just one is blocked, the other can still supply the liver.
The most common cause of blockage is a blood clot (thrombosis).
Hepatic artery clots can result from:
Injury to the artery (e.g., during liver transplantation)
An aneurysm (bulging of the artery wall)
Vasculitis (artery inflammation)
Cocaine use (artery spasm)
Sickle cell crisis
Emboli (clumps of material such as fat, tumor fragments, or clots breaking off from the heart or blood vessels and lodging in the hepatic artery)
Symptoms of Ischemic Hepatitis
Symptoms include nausea and vomiting. The liver may be tender and enlarged. If people already have severe scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), ischemic hepatitis can cause liver failure.
Diagnosis of Ischemic Hepatitis
Liver blood tests and blood-clotting tests
Sometimes imaging tests
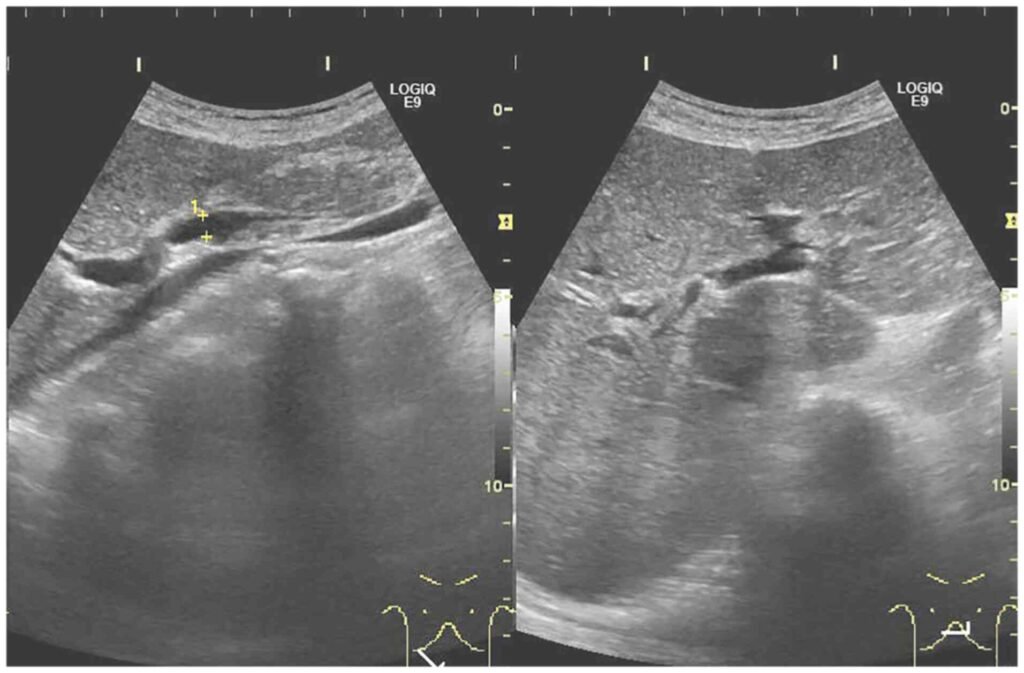
Doctors suspect ischemic hepatitis when results of liver blood tests (done to determine how well the liver is functioning and whether it is damaged) and/or blood clotting tests are abnormal in people who have a condition that can cause the disorder.
If doctors suspect ischemic hepatitis, they look for a cause. For example, they may do imaging tests to check heart function or for a blockage in the hepatic artery. These imaging tests include echocardiography, ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of blood vessels (magnetic resonance angiography), and arteriography, which involves taking x-rays after a radiopaque contrast agent (which is visible on x-rays) is injected into an artery.
Treatment of Ischemic Hepatitis
Address the root cause: The primary goal is to restore blood flow to the liver by improving cardiac output or reversing hemodynamic instability.
Supportive care: This may include managing the symptoms of the underlying condition, such as heart failure or sepsis.
Ischemic Hepatitis vs. Other Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is caused by viruses like Hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E, and can lead to inflammation.
Ischemic hepatitisis caused by a lack of blood and oxygen supply, leading to cell damage and death rather than direct viral inflammation.
Treatment of underlying condition
Doctors focus on treating the condition that is reducing blood flow to the liver. If blood flow can be restored, ischemic hepatitis commonly resolves.
